How Do Cavities Form? (Expert Advice)
Teeth are the hardest substances in the human body.
The enamel covering your teeth is even harder than bone, but like kryptonite and Superman, cavities are bad news for your teeth.
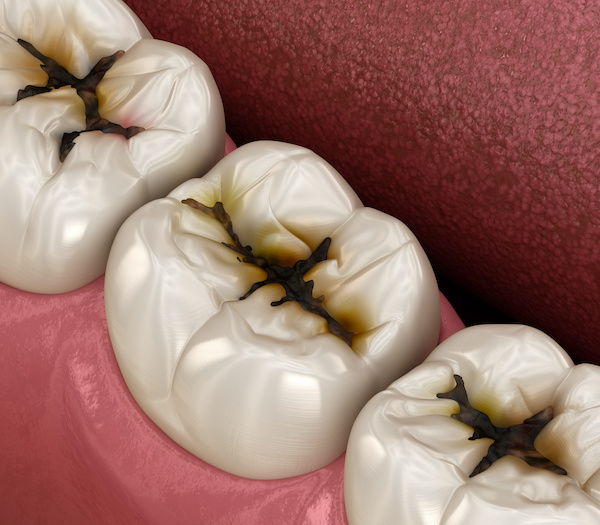
Cavities, or tooth decay, occur when acid produced in the mouth attacks the tooth causing holes or cavitations.
If left untreated, cavities can lead to toothache, infection, and tooth loss.
Understanding Cavities
Bacteria is always present in the mouth, and when proper oral hygiene is not maintained, bacterial flora will assemble into a thin, sticky substance known as plaque or biofilm.
Bacteria will then consume sugars from foods and beverages, leading to acid formation and cavities.
A tooth has three distinct layers that each serve a unique purpose.
Enamel
- Outer shell layer
- Calcium and phosphorus-rich
- Hardest tissue in body
Dentin
- Middle layer
- Porous and permeable
- Able to regenerate
Pulp
- Innermost layer
- Contains nerves and blood vessels
- Most sensitive area of tooth
The acid formation attacks the enamel first. Therefore, pain may not be elicited when cavities are contained in the enamel. The dentist may use a medicated fluoride paste to remineralize the decay if the cavity is discovered before bacteria creates a hole in the enamel.
Recommended Reading: Should You Use Prescription Fluoride Toothpaste? (Dentist’s Thoughts)Unfortunately, if left untreated, it will progress into the dentin leading to pain and irreversible damage.
Cavities can form on all surfaces of the teeth; however, the most common area is between the teeth.
Recommended Reading:
- Cavities | The Ultimate Guide (Content Hub)
- What Is a Cavity? What Causes Rotten Teeth?
- What Does a Cavity Look Like (20 Pictures)
- How to Fix a Cavity: Treatment Solutions & Costs
- Can You Reverse a Cavity (5 Simple Steps)
- 12 Cavity Risk Factors (Best Treatment)
- 10 Simple Steps to Prevent Cavities (Dentist’s Perspective)
- Why Does a Cavity Hurt? (5 Toothache Home Remedies)
Host
- Salivary flow
- Tooth anatomy
- Age
- Fluoride
- Oral hygiene
- Immune system
- Genetics
Bacteria
- Bacterial load
- Biofilm pH
Diet
- Nutrition
- Carbohydrate type
- Frequency of eating/drinking
Each factor plays a key role! Healthy foods have fewer fermentable carbohydrates leading to less acid production.
Sugar-rich foods are sticky and more difficult to clean, which leads to acid formation and attack on the teeth.
Saliva, however, will aid in removing acid if the salivary flow is sufficient.
Many medications will cause dry mouth leading to low salivary flow and decreased oral pH. Chewing sugar-free gum, using salivary stimulants (Biotene), or sipping water throughout the day will combat this process.
Lastly, some people are predisposed to cavities based on their genetic makeup and immune system response.
How to Limit Cavities
- Brush with an electric toothbrush twice a day
- Use fluoride toothpaste nightly
- Consume less carbohydrate-rich foods
- Limit snacking
- Chew sugar-free gum
- Sip on water to stimulate salivary flow
- Have sealants applied if necessary
- Drink sugar-rich beverages using straw
- Rinse with antiseptic mouthrinse nightly
- Floss regularly
- Use Waterpik for larger gaps between teeth
Diligent hygiene care and regular dental visits will aid in the prevention of cavities. Be sure to brush at least twice a day using an electric toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste.
Fluoride combines with calcium and phosphate to repair and restore weakened enamel. Floss regularly to clean away bacteria between your teeth.
This area is best cleaned with dental floss using a “c-shaped motion” around adjacent teeth. If you have more significant gaps between your teeth, a Waterpik is better.
Many people neglect this step, so “only floss the teeth you want to keep.”
Also, rinse with an ADA-approved antiseptic mouth rinse to disrupt the congregation of bacteria biofilm.
Recommended Reading: What is the ADA Seal of Acceptance?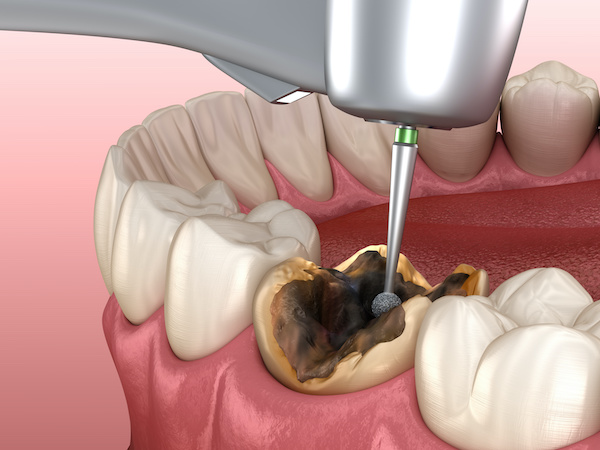
How Are Cavities Managed?
To formulate a preventive and restorative treatment plan, dentists utilize the patient’s medical history, x-rays, intra-oral photos, oral exam and oral hygiene habits.
Sealants may be applied to prevent decay in the pits and fissures of permanent molars.
The stages of decay are classified into five stages: E1, E2, D1, D2, and D3. For example, an E1 or E2 incipient cavity is located in the outer enamel layer.
Often, these cavities can be repaired using a prescription fluoride toothpaste such as Clinpro or Prevident 5000 ppm. If you are prone to cavities, you would be considered “high cavity risk.”
The dentist may suggest nightly fluoride trays to allow the fluoride to penetrate the enamel over an extended period.
High Cavity Risk Factors
- Poor oral hygiene
- Poor nutrition/diet
- Low salivary flow
- Multiple cavities
- Poor-fitting restorations
- Infrequent dental visits
- Weakened immune response
- Genetic predisposition
If the cavity has progressed into the dentin, the cavity will need to be removed and restored. If the tooth is still restorable, the tooth will require extensive treatment. If the tooth is deemed nonrestorable, an extraction is necessary to prevent the spread of infection.
Related: Best MDA Recommended ProductsThe most common tooth replacement options are implants, bridges, and partials.
My Experience & Expertise
Cavities can be a real pain, especially when you think you are doing enough to keep your teeth clean.
Have you recently visited the dentist to find yourself in this situation? Desire a second opinion?
My Dental Advocate’s team of board-certified dentists can provide a second opinion on your planned treatment. We look forward to bringing you peace of mind by verifying your treatment plan, suggesting an alternative, or answering your questions.
Need a second opinion? We can help! Learn more. Knowledge is power when cultivating healthy dental habits. The more informed you are, the better positioned you’ll be to prevent avoidable and potentially costly dental procedures for you and your family. Watch for future blog posts, where we’ll continue sharing important information, product reviews and practical advice!

About the Author
Dr. Matthew Hannan, also known as “Dr. Advocate,” is a board-certified dentist on a mission to provide accurate dental patient education. He attended Baylor University before completing dental school at UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry. He now lives in Arizona with his beautiful wife and 4 kids. Dr. Hannan believes everyone should access easy-to-read dental resources with relevant, up-to-date dental research and insight to improve their oral health.

Connect with Dr. Hannan!
CEREC Crowns | The Ultimate Guide (Content Hub)
CEREC crowns are same-day crowns that are fabricated in-office using CAD/CAM technology. This article is the content hub for CEREC crowns and is divided into seven sections. Each section links to another article…

Do ZeroWater Filters Remove Fluoride?
Water filtration systems have become a popular choice for many households looking to improve the quality of their drinking water. ZeroWater and Brita are two of the most well-known brands in the market, with millions of users worldwide. While Brita uses a basic filtration system, ZeroWater…

Dental X-rays | The Ultimate Guide (Content Hub)
In the vast realm of dentistry, one of the most revolutionary advancements has undoubtedly been the advent of dental X-rays. These powerful imaging tools have transformed how dental professionals diagnose, treat, and prevent oral conditions, granting a glimpse beneath the surface of the human mouth. This is the ultimate guide for dental X-rays. Below, you will find articles about dental X-rays from a dentist’s perspective.
Gain Clarity with Our FREE Second Opinion Guide
Receive clear, expert second opinions online within 48 hours. Start today!
Product Reviews
Our 250+ dental product reviews (and counting), curated by an experienced dentist, are the most comprehensive online.
Toothbrush Genie
State-of-the-art chatbot designed to help you discover your perfect toothbrush in just a few simple steps!
Cavity Risk Assessment
Cutting-edge digital tool designed to evaluate your individual cavity risk based on your responses to a series of questions.
Gum Disease Assessment
Discover your gum disease risk with our quick and engaging 6-question assessment!


