How to Read a Dental X-Ray (Dentist Tips)

Reading dental X-rays is crucial for dental professionals, offering insights into hidden oral health issues.
Mastering this skill involves understanding the anatomy displayed in different X-rays—like bitewings, periapicals, and panoramics.
Dentists must meticulously analyze them for irregularities such as cavities or gum disease.
With focused practice and a solid grasp of the fundamentals, you can excel in understanding dental X-rays the next time you’re at the dentist.
Need Dental Advice? Ask Dr. Hannan!
Key Takeaways
- Types of Dental X-Rays: Understanding the different kinds of X-rays—such as bitewing, periapical, and panoramic—is essential for targeted diagnosis. Each type serves a specific purpose, such as detecting cavities, bone loss, or impacted teeth.
- Interpreting X-ray Images: Recognizing the signs of healthy teeth and gums and abnormalities like cavities, gum disease, and bone loss is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Safety Measures: Dental X-rays involve exposure to low radiation levels, so safety precautions like the use of lead aprons and the cautious frequency of X-rays are essential. Special consideration should be given to pregnant patients to minimize risks. Digital X-rays are a safer, more efficient alternative to traditional X-rays.
Understanding the Basics of a Dental X-ray
A dental X-ray is a type of radiograph used to capture images of the teeth, gums, and bones in the mouth.
It is a valuable tool that allows dental professionals to diagnose and treat various dental conditions.
When you have a dental X-ray, a small sensor or film is placed in your mouth, and an X-ray machine is used to take pictures of your teeth.
The images produced can show the dentist or hygienist details that cannot be seen with the naked eye, such as cavities, bone loss, and impacted teeth.
There are two main types of dental X-rays: intraoral and extraoral. Intraoral X-rays are taken inside the mouth, providing detailed images of individual teeth and the surrounding bone.
Extraoral X-rays are taken outside the mouth, showing the entire mouth and jaw.
Dental X-rays use a very small amount of radiation, and the risk of harmful effects is extremely low. However, it is important to inform your dentist if you are pregnant or think you might be pregnant, as X-rays should be avoided during pregnancy unless absolutely necessary.
According to research, digital radiographs can reduce the amount of radiation exposure up to 80% compared to traditional film.
Dental X-rays are a safe and effective way to diagnose and treat dental problems.
By understanding how they work, you can feel more confident and knowledgeable about your dental care.
Identifying Different Types of Dental X-rays
When it comes to dental X-rays, there are several different types available.
Each type of X-ray is designed to capture a specific view of your teeth, gums, and jawbone.
Understanding the different types of dental X-rays can help you better understand your dental health and any potential issues that may arise.
Bitewing X-rays
- Bitewing X-rays are one of the most common types of dental X-rays.
- They are used to capture images of the upper and lower back teeth.
- Bitewing X-rays help detect cavities, decay, and bone loss.
- During a bitewing X-ray, you will be asked to bite down on a small piece of plastic while the X-ray machine captures images of your teeth.
Periapical X-rays
- Periapical X-rays capture images of individual teeth from the crown to the root.
- These X-rays help detect dental abscesses, cysts, and other abnormalities.
- During a periapical X-ray, a small film or digital sensor is placed inside your mouth while the X-ray machine captures images of your teeth.
Panoramic X-rays
- Panoramic X-rays capture a broad view of your entire mouth, including your teeth, gums, and jawbone.
- These X-rays help detect impacted teeth, jaw disorders, and oral cancer.
- During a panoramic X-ray, you will stand or sit while the machine rotates around your head, capturing images of your entire mouth.
Cephalometric X-rays
- Cephalometric X-rays are used to capture images of the entire head.
- These X-rays help detect facial asymmetry, jaw disorders, and sleep apnea.
- During a cephalometric X-ray, you will stand or sit while the machine captures images of your entire head.
Remember, each type of dental X-ray serves a specific purpose and is used to detect different issues. Your dentist will determine which type of X-ray is best for you based on your specific dental health needs.
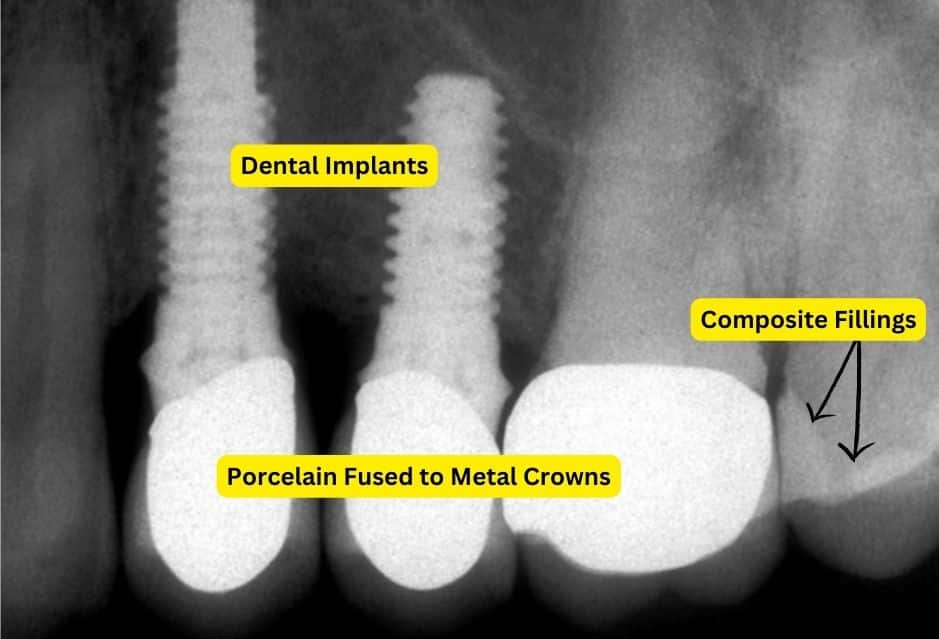
Interpreting Dental X-ray Images
X-rays are an essential diagnostic tool to help detect dental problems.
However, interpreting dental X-ray images can be challenging if you don’t know what to look for. In this section, we will guide you through interpreting dental X-ray images.
Recognizing Healthy Teeth and Gums
The first step in interpreting dental X-ray images is recognizing healthy teeth and gums. Healthy teeth and gums should appear as follows:
- Teeth should have a clear, white enamel layer and a dark, well-defined root.
- Gum tissue should be pink and firm, with a clear boundary between the teeth and gums.
If you notice any abnormalities in the teeth or gums, consult a dental professional.
Spotting Cavities and Tooth Decay
Cavities and tooth decay are common dental problems that can be detected through dental X-rays. Signs of cavities and tooth decay include:
- Dark spots or holes in the teeth.
- Changes in the enamel layer, such as thinning or roughness.
- Changes in the shape or size of the teeth.
Identifying Gum Disease and Bone Loss
Gum disease and bone loss are serious dental problems that can be detected through dental X-rays.
Signs of gum disease and bone loss include:
- Changes in the bone structure around the teeth, such as thinning or loss of bone.
- Changes in the gum tissue, such as swelling or redness.
- Changes in the position of the teeth, such as loose or shifting teeth.
In conclusion, interpreting dental X-ray images can be challenging, but with a basic understanding of what to look for, you can identify common dental problems and seek appropriate treatment.
Understanding Dental X-ray Safety
Dental X-rays are essential for diagnosing and treating dental problems. However, X-rays use radiation, which can be harmful if not used safely. Here are some things you should know about dental X-ray safety:
Frequency of X-rays
- Your dentist should determine the frequency of dental X-rays based on your needs.
- Depending on their dental history and current dental health, some may require X-rays more frequently than others.
- Your dentist should only recommend X-rays when necessary to avoid unnecessary radiation exposure.
Radiation Exposure
- Dental X-rays use low radiation levels, but minimizing exposure is still important.
- Your dentist should use lead aprons and thyroid collars to protect your body from unnecessary radiation.
- If you are pregnant, you should inform your dentist before any X-rays are taken, as there is a risk of harm to the developing fetus.
Digital X-rays
- Digital X-rays use less radiation than traditional X-rays and are more environmentally friendly.
- They also provide clearer images that can be enhanced and manipulated for better diagnosis and treatment planning.
- If your dentist offers digital X-rays, it may be a safer and more efficient option for you.
In some cases, X-rays may not be necessary. Your dentist may be able to diagnose and treat your dental problems without using X-rays. However, if X-rays are necessary, your dentist will take precautions to ensure your safety.
Dental X-rays are a safe and important tool for diagnosing and treating dental problems.
By understanding dental X-ray safety, you can ensure that you receive the necessary care while minimizing your radiation exposure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Why do I need a dental X-ray?
Dental X-rays help your dentist see issues that aren’t visible to the naked eye. This can include early-stage cavities, gum disease, or other abnormalities. They are essential tools for diagnosis and treatment planning.
How often should I get dental X-rays?
The frequency of dental X-rays varies from person to person based on their oral health. Some might need X-rays every six months, while others might only need them every couple of years. Your dentist will recommend a schedule that’s appropriate for you.
Do dental X-rays hurt?
Dental X-rays are generally painless. You might feel some discomfort from holding the X-ray film or sensor in your mouth, but the process is quick and doesn’t involve any kind of pain.
My Experience & Expertise
By now, you should better understand how to read a dental X-ray.
Remember that interpreting X-rays is a complex task that requires a trained eye and a thorough understanding of anatomy and pathology.
While this guide can help you get started, it is not a substitute for professional training and experience.
Key Takeaways
- Always start by checking the patient’s information and the type of X-ray you are looking at.
- Look for any abnormalities or irregularities in the teeth, gums, bone, and surrounding tissues.
- Use the ABCDE approach to analyze each X-ray systematically and avoid missing important findings.
- Pay attention to the quality of the X-ray, including the exposure, contrast, and resolution.
- When interpreting X-rays, consider the patient’s medical and dental history, symptoms, and clinical examination findings.
- Document your findings accurately and clearly, and communicate them effectively to the patient and other healthcare providers.
Need a second opinion? We can help! Learn more. Knowledge is power when cultivating healthy dental habits. The more informed you are, the better positioned you’ll be to prevent avoidable and potentially costly dental procedures for you and your family. Watch for future blog posts, where we’ll continue sharing important information, product reviews and practical advice!

About the Author
Dr. Matthew Hannan, also known as “Dr. Advocate,” is a board-certified dentist on a mission to provide accurate dental patient education. He attended Baylor University before completing dental school at UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry. He now lives in Arizona with his beautiful wife and 4 kids. Dr. Hannan believes everyone should access easy-to-read dental resources with relevant, up-to-date dental research and insight to improve their oral health.

Connect with Dr. Hannan!

5 Best Fluoride-Free Mouthwash 2024 (Dentist Recommended)
In the quest for optimal oral health, we increasingly find ourselves at the crossroads of choice. The products we use daily can significantly impact our overall health, and mouthwash is no exception. As more research emerges on the pros and cons of fluoride, many are exploring fluoride-free alternatives for our dental hygiene routine.

Philips Sonicare 1100 vs. 2100 Electric Toothbrush Review
Are you trying to decide between the Philips Sonicare 1100 and 2100 electric toothbrushes? With so many options on the market, it can be challenging to determine which toothbrush is the best fit for your needs…

Pregnancy Gingivitis (Causes, Symptoms & Treatment 2024)
Pregnancy and the baby’s development inside a mother’s womb is a beautiful miracle; however, it doesn’t come without swollen legs, body aches and labor pains. In addition, hormones are in constant flux, preparing the mother for the baby’s arrival. Progesterone and estrogen…
Gain Clarity with Our FREE Second Opinion Guide
Receive clear, expert second opinions online within 48 hours. Start today!
Product Reviews
Our 250+ dental product reviews (and counting), curated by an experienced dentist, are the most comprehensive online.
Toothbrush Genie
State-of-the-art chatbot designed to help you discover your perfect toothbrush in just a few simple steps!
Cavity Risk Assessment
Cutting-edge digital tool designed to evaluate your individual cavity risk based on your responses to a series of questions.
Gum Disease Assessment
Discover your gum disease risk with our quick and engaging 6-question assessment!


