Expert Pediatric Dental X-ray Guidelines (Complete Guide)

Every parent wants what’s best for their child, especially their health. But dental visits can bring up questions, especially around the topic of x-rays.
Are they safe? How often are they needed? What’s the real purpose behind them?
Key Takeaways
- Understanding Pediatric X-rays: Dental X-rays are critical tools for diagnosing and monitoring oral health issues in children. Knowledge of their guidelines ensures effective management of a child’s dental health.
- Importance of X-rays: They play a pivotal role in the early detection of issues like tooth decay, abnormal tooth development, cysts, or tumors, helping to avoid extensive future treatments.
- Safety and Guidelines: Minimizing radiation exposure and prioritizing patient safety is crucial. Adherence to the ALARA principle and using protective gear like lead aprons are essential.
Importance of Pediatric Dental X-Ray
Early Detection
Pediatric dental X-rays provide valuable insights into your child’s oral health. By detecting issues early, you can take preventive measures to avoid complications.
Need Dental Advice? Ask Dr. Hannan!
For instance, dental X-rays can identify tooth decay hidden between teeth or below the gum line, which is not visible during a routine dental examination.
Additionally, X-rays help detect abnormal tooth development, such as impacted or extra teeth, and determine the presence and size of cysts or tumors.
This early detection helps avoid extensive dental treatments later in your child’s life.
Effective Treatment Planning
When dental problems are identified during their early stages, pediatric dentists can develop more accurate treatment plans.
For example, dental X-rays will reveal the underlying issues if your child has a misaligned bite or overcrowded teeth, allowing the dentist to suggest suitable orthodontic treatments.
Moreover, dental X-rays can be used to assess the success of ongoing dental treatments and make adjustments if needed.
This ensures your child receives the most effective care for their dental needs.
According to research, digital radiographs can reduce the amount of radiation exposure up to 80% compared to traditional film.
General Guidelines for Pediatric Dental X-Ray
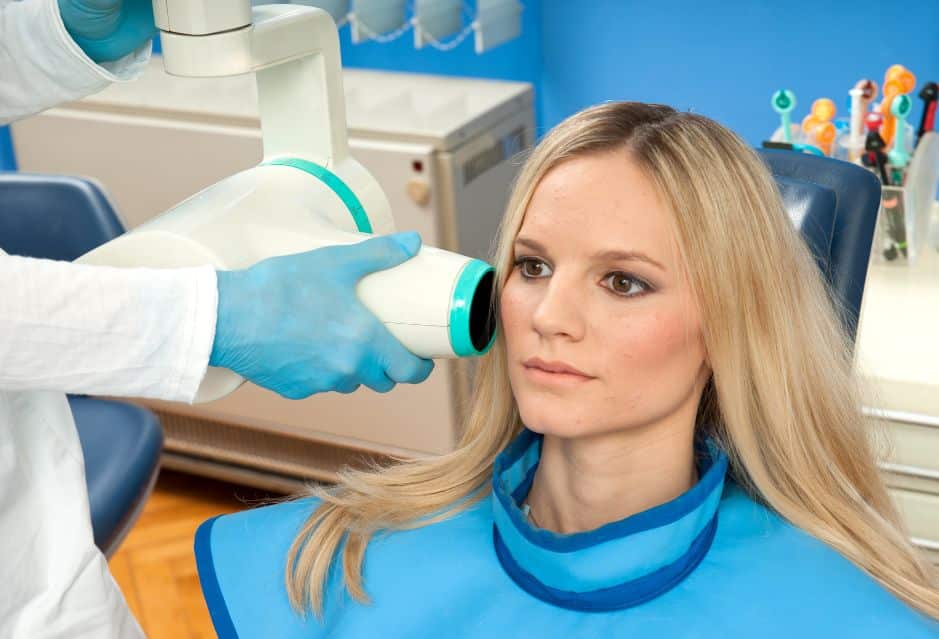

Here are some general guidelines for pediatric dental x-ray:
1. Determine the necessity of X-rays: Avoid taking unnecessary X-rays. Consult with a pediatric dentist to decide if X-rays are essential for your patient’s case. Consider the child’s age, dental history, and risk of dental issues.
2. Adapt to the child’s size and stage of development: Use appropriately sized film or sensors for children of different ages. Ensure proper positioning and patient comfort to minimize retakes and radiation exposure.
3. Opt for low-exposure techniques: Use digital X-ray systems and faster film speeds to minimize the radiation dose. Adjust exposure settings to account for a child’s smaller size. Always use lead aprons and thyroid collars to protect the patient from radiation exposure.
4. Consider discussing with parents in advance: Informing the parents about the necessity and safety guidelines of dental X-rays can alleviate potential concerns.
5. Frequency of dental X-rays: Follow professional and evidence-based recommendations for the frequency of x-rays depending on the child’s risk assessment and dental development. Periodically reassess the child’s needs as they grow to adjust the x-ray schedule accordingly.
Recommended Reading: How Often Should You Get Dental X-rays (Expert Advice)Adhering to these general guidelines ensures pediatric dental X-rays are conducted safely, efficiently, and effectively in your dental practice.
Determining the Frequency of Pediatric Dental X-rays
Dental X-rays are invaluable in the early detection of oral health issues in children, providing insights that might be invisible to the naked eye.
But the question arises: How often should these X-rays be taken? Striking the right balance is essential to ensure pediatric patients’ safety and health.
Child’s Oral Health Status
- Low Risk: Children with no history of cavities or other dental issues and who maintain regular dental hygiene may need x-rays less frequently.
- High Risk: Those with a history of cavities, dental trauma, or other oral issues may require more frequent monitoring.
Age & Developmental Stages
- Primary Teeth: Before permanent teeth emerge, x-rays might be taken to monitor the development of primary teeth and identify any potential issues.
- Mixed Dentition: As children lose their primary teeth and permanent teeth emerge, x-rays can help track their progress and ensure proper spacing and alignment.
- Teenagers: With the emergence of wisdom teeth and other adult teeth, periodic X-rays can assist in early identification of impactions or misalignments.
Baseline Establishment
It’s common for dentists to recommend a set of X-rays when a child visits the dental clinic for the first time. This serves as a baseline to compare with future X-rays.
Symptomatic Cases
Irrespective of the set schedule, if a child presents with symptoms like pain, swelling, or trauma, an x-ray might be immediately necessary to diagnose the underlying issue.
Recommendations by Experts
The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) suggests varying frequencies based on risk. For instance, children with a high risk of cavities might need posterior bitewing x-rays every 6-12 months, while those at low risk might only need them every 12-24 months.
Adherence to ALARA
Dentists always keep the ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle in mind. This means that x-rays are only recommended when a clear diagnostic benefit outweighs the minimal risk of radiation exposure.
Safety Measures in Pediatric Dental X-Ray
Radiation Protection
When performing a pediatric dental x-ray, it is essential to prioritize the patient’s safety by minimizing radiation exposure.
Ensure to follow the ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) and adhere to the established guidelines.
Helpful Tips
- Use high-speed film or digital sensors to reduce exposure time.
- Utilize lead aprons and thyroid collars as shielding devices.
- Update your X-ray equipment regularly for optimal function.
- Tailor exposure settings according to the patient’s size and age.
Patient Comfort
Keeping the young patient comfortable during the X-ray process is crucial for a successful and stress-free experience.
Recommendations
- Communicate openly with the child and their parent or guardian about the procedure.
- Use appropriately-sized film holders and bite-wings.
- Allow the parent or guardian to remain in the room, when possible.
- Offer distraction techniques such as gentle music or visual stimuli.
Identifying Gum Disease and Bone Loss
Gum disease and bone loss are serious dental problems that can be detected through dental X-rays.
Signs & Symptoms
- Changes in the bone structure around the teeth, such as thinning or loss of bone.
- Changes in the gum tissue, such as swelling or redness.
- Changes in the position of the teeth, such as loose or shifting teeth.
Unique Considerations in Pediatric Patients
Regarding pediatric dental X-rays, there are some unique considerations you should be aware of as they pertain to children specifically.
Firstly, children’s teeth are more susceptible to decay compared to adults. This is due to the thinner and less resistant enamel on their teeth. As a result, dental x-rays are a crucial tool to identify early signs of tooth decay before it progress and causes further harm.
Next, the size and position of children’s teeth can vary significantly compared to adult teeth. This makes diagnosing dental issues more challenging.
Dental X-rays provide necessary detailed information about the tooth and its surrounding tissues, allowing for more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
Also, children’s teeth and jaws are constantly developing and growing. Monitoring this growth through dental X-rays can help identify any issues with the growth and development, such as malocclusion or impaction.
Early detection and intervention can help prevent long-term complications.
In terms of safety, it is important to note that radiation exposure during pediatric dental X-rays is minimal. To further reduce this exposure, dentists follow the ALARA principle, “As Low As Reasonably Achievable”.
This involves using appropriate shielding, employing lower radiation settings, and only taking X-rays when necessary.
Highlights
- Higher susceptibility to decay
- Varied size and position of teeth
- Monitoring growth and development
- Minimal radiation exposure with adherence to safety guidelines
Techniques for Pediatric Dental X-Rays
When performing dental X-rays on children, it’s essential to use the correct techniques to ensure their safety and comfort. You can use the following techniques to carry out pediatric dental X-rays effectively.
First, explain the procedure to the child and their parents before starting. This helps alleviate any anxiety and provides an opportunity to answer any questions. Opt for age-appropriate language and reassure the child that the process is quick and painless.
Next, use appropriate protective gear such as lead aprons and thyroid collars. These provide added protection against radiation exposure, particularly for young patients who may be more radiation-sensitive. Verify that the protective gear is in good condition and fits the child properly.
It’s vital to select the correct X-ray technique. The two most commonly used methods for pediatric dental X-rays are the intraoral and extraoral techniques. Intraoral X-rays involve the placement of a sensor inside the child’s mouth.
The bitewing, periapical, and occlusal variations focus on different sections of the teeth and surrounding tissues. Extraoral X-rays, like panoramic or cephalometric, capture images without inserting a sensor into the child’s mouth.
Always utilize the lowest possible radiation dose that offers a quality diagnostic image. Ensure the X-ray machine is functioning well and calibrated for the specific age and size of the pediatric patient.
Using rectangular collimation and digital sensors can further help minimize radiation exposure.
Lastly, engage in effective patient positioning. Encourage the child to sit still and provide clear instructions. You may want to use bite blocks or stabilizing devices if the child struggles with stabilization.
Maintain open communication with the child during the x-ray and offer praise to help create a positive experience.
Interpreting Pediatric Dental X-Rays
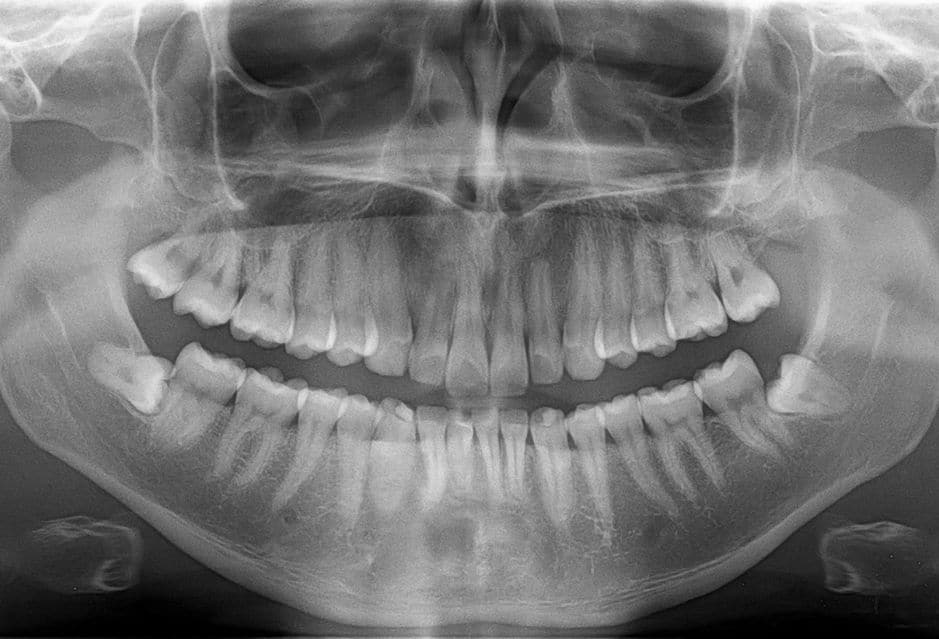
When interpreting pediatric dental X-rays, you should start by evaluating the quality of the radiograph. Ensure it is error-free, properly focused, and displays the necessary anatomical structures.
Your assessment should involve systematic examination to avoid overlooking any important information.
First, evaluate the hard tissues of your patient’s mouth, including teeth and supporting structures.
Examine the enamel, dentin, and pulp, inspecting for any signs of decay, fractures, or abnormalities.
Assess the periodontal ligament space and the lamina dura for any signs of infection or inflammation.
Next, examine the developing teeth, ensuring appropriate positioning, size, and formation. Check for any missing, impacted, or supernumerary teeth, as these can affect a child’s dental development.
Key Factors
- Tooth eruption: Check the sequence and timing of tooth eruption to ensure it aligns with your patient’s age and development stage.
- Root development: Assess the root-to-crown ratio, as premature tooth loss might lead to complications in permanent dentition.
- Spacing: Observe the space available for unerupted teeth to avoid crowding and other dental malocclusions.
When analyzing the surrounding soft tissues, identify any pathological changes, such as cysts, tumors, or infections. Review the temporomandibular joint for any structural abnormalities that could interfere with a patient’s bite function.
Lastly, don’t forget to consider your patient’s age and the relevance of radiographic findings when creating a treatment plan. Some conditions might require immediate intervention, while others may not, depending on factors like your patient’s development stage.
Keep in mind to use your professional judgement and adapt your recommendations based on each case’s individual needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Are dental x-rays safe for children, and what precautions are taken to ensure their safety?
Yes, dental x-rays are safe for children. Dentists follow the ALARA principle (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) to ensure that radiation exposure is minimal. Protective measures, such as the use of lead aprons and thyroid collars, are employed. Furthermore, modern dental x-ray equipment, especially digital systems, emit extremely low doses of radiation, which is even further reduced for pediatric patients based on their size.
How often should a child get dental x-rays?
The frequency of dental x-rays largely depends on the child’s oral health, age, risk for disease, and the stage of dental development. The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry (AAPD) provides guidelines which dentists follow, but typically, if a child is at a higher risk for dental problems, they may require x-rays more frequently to monitor conditions.
What’s the difference between intraoral and extraoral x-ray techniques?
Intraoral x-rays involve placing the x-ray film or sensor inside the child’s mouth, capturing detailed images of individual teeth and their supporting structures. Common types include bitewing, periapical, and occlusal x-rays. Extraoral x-rays, on the other hand, are taken from outside the mouth. They provide broader views, capturing overall dental structures, jaws, and even the skull. Panoramic and cephalometric x-rays are common types of extraoral x-rays.
My Experience & Expertise
As a dentist, understanding pediatric dental x-ray guidelines is pivotal.
Ensuring adherence safeguards children’s health and elevates the quality of your services. Embrace the ALARA principle to minimize radiation risks, complemented by using protective gear like lead aprons and thyroid collars.
The need for X-rays should be evaluated based on individual dental history and risk factors, nurturing trust with caregivers. Keep abreast of advancements, engage in continuous learning, and maintain open dialogues with parents, enhancing your contribution to children’s oral well-being.
Need a second opinion? We can help! Learn more. Knowledge is power when cultivating healthy dental habits. The more informed you are, the better positioned you’ll be to prevent avoidable and potentially costly dental procedures for you and your family. Watch for future blog posts, where we’ll continue sharing important information, product reviews and practical advice!

About the Author
Dr. Matthew Hannan, also known as “Dr. Advocate,” is a board-certified dentist on a mission to provide accurate dental patient education. He attended Baylor University before completing dental school at UT Health San Antonio School of Dentistry. He now lives in Arizona with his beautiful wife and 4 kids. Dr. Hannan believes everyone should access easy-to-read dental resources with relevant, up-to-date dental research and insight to improve their oral health.

Connect with Dr. Hannan!

Best Dental Advice (Dentist Perspective) | Part 2
According to a recent study, Only 25.8% of children reported a high oral health knowledge. Yet, we have many resources to learn about healthy dental habits, revolutionary dental products, and preferred dental treatments. After years…
How Much Are CEREC Crowns? (Pros, Cons & Treatment Cost)
Treatment cost for CEREC crowns varies depending on where you live and the dentist’s credentials, but it is typically more expensive than getting traditional crowns. This blog post will discuss the pros and cons…

Dental X-rays | The Ultimate Guide (Content Hub)
In the vast realm of dentistry, one of the most revolutionary advancements has undoubtedly been the advent of dental X-rays. These powerful imaging tools have transformed how dental professionals diagnose, treat, and prevent oral conditions, granting a glimpse beneath the surface of the human mouth. This is the ultimate guide for dental X-rays. Below, you will find articles about dental X-rays from a dentist’s perspective.
Gain Clarity with Our FREE Second Opinion Guide
Receive clear, expert second opinions online within 48 hours. Start today!
Product Reviews
Our 250+ dental product reviews (and counting), curated by an experienced dentist, are the most comprehensive online.
Toothbrush Genie
State-of-the-art chatbot designed to help you discover your perfect toothbrush in just a few simple steps!
Cavity Risk Assessment
Cutting-edge digital tool designed to evaluate your individual cavity risk based on your responses to a series of questions.
Gum Disease Assessment
Discover your gum disease risk with our quick and engaging 6-question assessment!


